- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Oxaliplatin-incorporated micelles eliminate both cancer stem-like and bulk cell populations in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Purpose
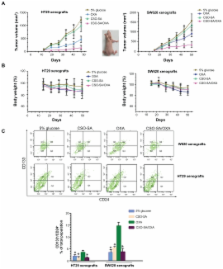
The failure of cancer treatments is partly due to the enrichment of cancer stem-like cells (CSLCs) that are resistant to conventional chemotherapy. A novel micelle formulation of oxaliplatin (OXA) encapsulated in chitosan vesicle was developed. The authors postulate that micelle encapsulation of OXA would eliminate both CSLCs and bulk cancer cells in colorectal cancer (CRC).
Experimental design
In this study, using stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide (CSO-SA) polymeric micelles as a drug-delivery system, OXA-loaded CSO-SA micelles (CSO-SA/OXA) were prepared. Intracellular uptake of CSO-SA/OXA micelles was assessed by confocal microscope. The effects of free OXA, the empty carrier, and CSO-SA/OXA micelles were tested using human CRC cell lines in vitro and in vivo.
Results
The micelles showed excellent internalization ability that increased OXA accumulation both in CRC cells and tissues. Furthermore, CSO-SA/OXA micelles could either increase the cytotoxicity of OXA against the bulk cancer cells or reverse chemoresistance of CSLC subpopulations in vitro. Intravenous administration of CSO-SA/OXA micelles effectively suppressed the tumor growth and reduced CD133 +/CD24 + cell (putative CRC CSLC markers) compared with free OXA treatment, which caused CSLC enrichment in xenograft tumors ( P < 0.05).