- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Synthetic Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside Attenuates Established Pain, Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in a Rodent Model of Painful Radiculopathy
Read this article at
Abstract
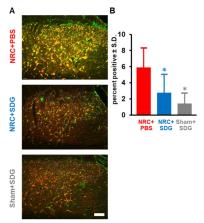
Painful cervical radiculopathy is characterized by chronic neuroinflammation that lowers endogenous antioxidant responses leading to the development of oxidative stress and pain after neural trauma. Therefore, antioxidants such as secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), that promote antioxidant signaling and reduce oxidative damage may also provide pain relief. This study investigated if repeated systemic administration of synthetic SDG after a painful root compression reduces the established pain, oxidative stress and spinal glial activation that are typically evident. SDG was administered on days 1–3 after compression and the extent of oxidative damage in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and spinal cord was measured at day 7 using the oxidative stress markers 8-hydroxguanosine (8-OHG) and nitrotyrosine. Spinal microglial and astrocytic activation were also separately evaluated at day 7 after compression. In addition to reducing pain, SDG treatment reduced both spinal 8-OHG and nitrotyrosine, as well as peripheral 8-OHG in the DRG. Moreover, SDG selectively reduced glial activation by decreasing the extent of astrocytic but not microglial activation. These findings suggest that synthetic SDG may attenuate existing radicular pain by suppressing the oxidative stress and astrocytic activation that develop after painful injury, possibly identifying it as a potent therapeutic for painful radiculopathies.
Related collections
Most cited references75
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found