- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
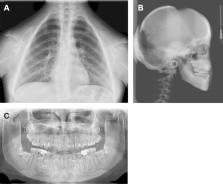
Craniofacial features of cleidocranial dysplasia
Read this article at
Abstract
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is an autosomal-dominant malformation syndrome affecting bones and teeth. The most common skeletal and dental abnormalities in affected individuals are hypoplastic/aplastic clavicles, open fontanelles, short stature, retention of primary teeth, delayed eruption of permanent teeth, supernumerary teeth, and multiple impacted teeth. Treatment of CCD requires a multidisciplinary approach that may include dental corrections, orthognathic surgery and cranioplasty along with management of any complications of CCD. Early diagnosis of this condition enables application of the treatment strategy that provides the best quality of life to such patients. Notably, Runx2 gene mutations have been identified in CCD patients. Therefore, further elucidation of the molecular mechanism of supernumerary teeth formation related to Runx2 mutations may improve understanding of dental development in CCD. The insights into CCD pathogenesis may assist in the development of new treatments for CCD.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Missense mutations abolishing DNA binding of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor OSF2/CBFA1 in cleidocranial dysplasia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cleidocranial dysplasia: clinical and molecular genetics.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found