- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Novel Omega-6 Fatty Acid Docosapentaenoic Acid Positively Modulates Brain Innate Immune Response for Resolving Neuroinflammation at Early and Late Stages of Humanized APOE-Based Alzheimer's Disease Models
Read this article at
Abstract
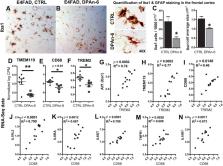
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD), in which activated microglia are found to be associated with neurodegeneration. However, there is limited evidence showing how neuroinflammation and activated microglia are directly linked to neurodegeneration in vivo. Besides, there are currently no effective anti-inflammatory drugs for AD. In this study, we report on an effective anti-inflammatory lipid, linoleic acid (LA) metabolite docosapentaenoic acid (DPAn-6) treatment of aged humanized EFAD mice with advanced AD pathology. We also report the associations of neuroinflammatory and/or activated microglial markers with neurodegeneration in vivo. First, we found that dietary LA reduced proinflammatory cytokines of IL1-β, IL-6, as well as mRNA expression of COX2 toward resolving neuroinflammation with an increase of IL-10 in adult AD models E3FAD and E4FAD mice. Brain fatty acid assays showed a five to six-fold increase in DPAn-6 by dietary LA, especially more in E4FAD mice, when compared to standard diet. Thus, we tested DPAn-6 in aged E4FAD mice. After DPAn-6 was administered to the E4FAD mice by oral gavage for three weeks, we found that DPAn-6 reduced microgliosis and mRNA expressions of inflammatory, microglial, and caspase markers. Further, DPAn-6 increased mRNA expressions of ADCYAP1, VGF, and neuronal pentraxin 2 in parallel, all of which were inversely correlated with inflammatory and microglial markers. Finally, both LA and DPAn-6 directly reduced mRNA expression of COX2 in amyloid-beta42 oligomer-challenged BV2 microglial cells. Together, these data indicated that DPAn-6 modulated neuroinflammatory responses toward resolution and improvement of neurodegeneration in the late stages of AD models.
Related collections
Most cited references77
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
voom: precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found