- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: transmission, virology and therapeutic targeting to aid in outbreak control
Read this article at
Abstract
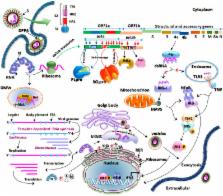
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes high fever, cough, acute respiratory tract infection and multiorgan dysfunction that may eventually lead to the death of the infected individuals. MERS-CoV is thought to be transmitted to humans through dromedary camels. The occurrence of the virus was first reported in the Middle East and it subsequently spread to several parts of the world. Since 2012, about 1368 infections, including ~487 deaths, have been reported worldwide. Notably, the recent human-to-human ‘superspreading' of MERS-CoV in hospitals in South Korea has raised a major global health concern. The fatality rate in MERS-CoV infection is four times higher compared with that of the closely related severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Currently, no drug has been clinically approved to control MERS-CoV infection. In this study, we highlight the potential drug targets that can be used to develop anti-MERS-CoV therapeutics.
Related collections
Most cited references79
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found