- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Non-sustained Ventricular Tachycardia as a Presentation of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy

Read this article at
Abstract
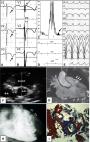
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is a rare disorder with familial (autosomal dominant) predisposition and can be challenging to diagnose. Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT) is a relatively uncommon and short-lived arrhythmia when seen in the general, healthy population. NSVT with a left bundle branch block morphology is usually idiopathic but may also be seen in ARVC. It can also be associated with poorer prognosis and increased mortality. Repetitive monomorphic ventricular ectopic beats may suggest ARVC, but could also be idiopathic. Timely diagnosis is vital due to the unpredictability and progressive nature of ARVC. We present a case of a 40-year-old Caucasian female with heart palpitations and NSVT found on an outpatient Holter monitor, and later found to have clinical and radiological features consistent with ARVC.
Related collections
Most cited references8
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
2019 HRS expert consensus statement on evaluation, risk stratification, and management of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Right ventricular dysplasia: a report of 24 adult cases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found