- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of the Immune Response in the Development of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Read this article at
Abstract
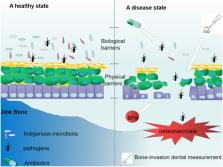
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a rare but serious adverse drug effect. There are multiple hypotheses to explain the development of MRONJ. Reduced bone remodeling and infection or inflammation are considered central to the pathogenesis of MRONJ. In recent years, increasing evidence has shown that bisphosphonates (BPs)-mediated immunity dysfunction is associated with the pathophysiology of MRONJ. In a healthy state, mucosal immunity provides the first line of protection against pathogens and oral mucosal immune cells defense against potentially invading pathogens by mediating the generation of protective immunoinflammatory responses. In addition, the immune system takes part in the process of bone remodeling and tissue repair. However, the treatment of BPs disturbs the mucosal and osteo immune homeostasis and thus impairs the body's ability to resist infection and repair from injury, thereby adding to the development of MRONJ. Here, we present the current knowledge about immunity dysfunction to shed light on the role of local immune disorder in the development of MRONJ.
Related collections
Most cited references117
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Origin and physiological roles of inflammation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found