- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neurobiology of Acupuncture: Toward CAM
Read this article at
Abstract
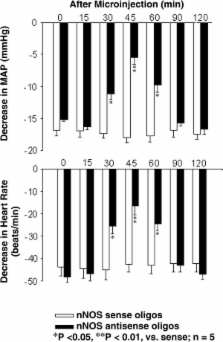
It has long been accepted that acupuncture, puncturing and scraping needles at certain points on the body, can have analgesic and anesthetic effects, as well as therapeutic effects in the treatment of various diseases. This therapy, including acupuncture anesthesia, has drawn the attention of many investigators and become a research subject of international interest around the world. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the nervous system, neurotransmitters, endogenous substances and Jingluo (meridians) may respond to needling stimulation and electrical acupuncture. An abundance of information has now accumulated concerning the neurobiological mechanisms of acupuncture, in relation to both neural pathways and neurotransmitters/hormonal factors that mediate autonomic regulation, pain relief and other therapeutics. Early studies demonstrated that the analgesic effects of electroacupuncture (EA) are mediated by opioid peptides in the periaqueductal gray. Recent evidence shows that nitric oxide plays an important role in mediating the cardiovascular responses to EA stimulation through the gracile nucleus-thalamic pathway. Other substances, including serotonin, catecholamines, inorganic chemicals and amino acids such as glutamate and α-aminobutyric acid (GABA), are proposed to mediate certain cardiovascular and analgesic effects of acupuncture, but at present their role is poorly understood. The increased interest in acupuncture health care has led to an ever-growing number of investigators pursuing research in the processes of the sense of needling touch, transduction of needling stimulation signals, stimulation parameters and placebos. In this Review, the evidence and understanding of the neurobiological processes of acupuncture research have been summarized with an emphasis on recent developments of nitric oxide mediating acupuncture signals through the dorsal medulla-thalamic pathways.
Related collections
Most cited references95
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Introducing a placebo needle into acupuncture research.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Placebo controls for acupuncture studies.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
