- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Measurement of normal patellar ligament and anterior cruciate ligament by MRI and data analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
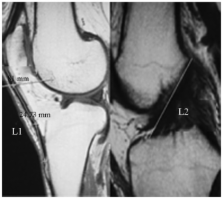
The aim of this study was to obtain geometric data of in vivo patellar ligament (PL) and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) by MRI and to analyze the correlation of the two with body weight, height and gender. A total of 157 cases with normal sagittal images of bilateral PL and ACL were enrolled. The PL and ACL lengths in the images were measured using the Radworks 5.1 application. The intraclass correlation coefficient for the data measured independently by three doctors was 0.997–1.000. In individuals aged 15–24 years, the values of PL and ACL length and the PL to ACL ratio were 43.95±4.25 mm, 38.45±4.62 mm and 1.15±1.09 in males and 42.03±0.94 mm, 36.00±1.06 mm and 1.18±0.1 in females, respectively. In individuals aged 25–64 years, the values in males were 40.99±4.45 mm, 36.06±3.74 mm and 1.14±0.09 and in females were 39.84±0.64 mm, 36.50±0.81 mm and 1.11±0.02, respectively. In individuals aged ≥65 years, the values in males were 41.43±3.08 mm, 36.62±3.44 mm and 1.15±0.09 and in females were 38.94±0.79 mm, 34.36±0.85 mm and 1.13±0.07, respectively. There was a significant difference between PL and ACL length on the same side (P<0.01). The data obtained was stable and repeatable. The present study established a database of PL and ACL length and the ratio of the two measured by MRI.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Biomechanical analysis of human ligament grafts used in knee-ligament repairs and reconstructions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ligament length relationships in the moving knee.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found