- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anti-Cancer Effect of Cordycepin on FGF9-Induced Testicular Tumorigenesis
Read this article at
Abstract
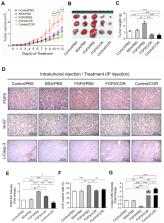
Cordycepin, a bioactive constituent from the fungus Cordyceps sinensis, could inhibit cancer cell proliferation and promote cell death via induction of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy. Our novel finding from microarray analysis of cordycepin-treated MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells is that cordycepin down-regulated the mRNA levels of FGF9, FGF18, FGFR2 and FGFR3 genes in MA-10 cells. Meanwhile, the IPA-MAP pathway prediction result showed that cordycepin inhibited MA-10 cell proliferation by suppressing FGFs/FGFRs pathways. The in vitro study further revealed that cordycepin decreased FGF9-induced MA-10 cell proliferation by inhibiting the expressions of p-ERK1/2, p-Rb and E2F1, and subsequently reducing the expressions of cyclins and CDKs. In addition, a mouse allograft model was performed by intratumoral injection of FGF9 and/or intraperitoneal injection of cordycepin to MA-10-tumor bearing C57BL/6J mice. Results showed that FGF9-induced tumor growth in cordycepin-treated mice was significantly smaller than that in a PBS-treated control group. Furthermore, cordycepin decreased FGF9-induced FGFR1-4 protein expressions in vitro and in vivo. In summary, cordycepin inhibited FGF9-induced testicular tumor growth by suppressing the ERK1/2, Rb/E2F1, cell cycle pathways, and the expressions of FGFR1-4 proteins, suggesting that cordycepin can be used as a novel anticancer drug for testicular cancers.
Related collections
Most cited references73

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Combination therapy in combating cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found