- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inflammatory myopathy with myasthenia gravis : Thymoma association and polymyositis pathology
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
To provide evidence that idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IM) with myasthenia gravis (MG) frequently shows thymoma association and polymyositis (PM) pathology and shares clinicopathologic characteristics with IM induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
Methods
We analyzed the clinicopathologic features of 10 patients with idiopathic IM and MG identified in 970 consecutive patients with biopsy-proven IM.
Results
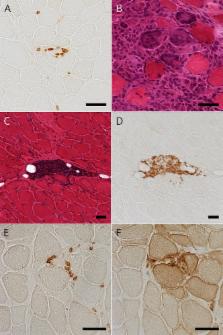
Seven patients (70%) had thymoma. IM and MG were diagnosed with more than 5-year time difference in 6 thymomatous patients and within 1 year in 1 thymomatous and 3 nonthymomatous patients. Seven thymomatous patients showed rhabdomyolysis-like features with respiratory failure (4/7), dropped head (3/7), cardiac involvement (2/7), and positive anti–acetylcholine receptor (anti-AChR) and anti-titin antibodies (7/7 and 4/6, respectively) but rarely showed ocular symptoms (2/7) or decremental repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) responses (1/7) at IM diagnosis. Three nonthymomatous patients showed acute cardiorespiratory failure with rhabdomyolysis-like features (1/3), positive anti-AChR and anti-titin antibodies (3/2 and 2/2, respectively), and fluctuating weakness of the skeletal muscle without ocular symptoms (3/3). Muscle pathology showed a PM pathology with infiltration of CD8-positive CD45RA-negative T-lymphocytes (9/9), scattered endomysial programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)–positive cells (9/9), and overexpression of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) on the sarcolemma of muscle fibers around the infiltrating PD-1–positive cells (7/9).
Conclusion
Rhabdomyolysis-like features, positive anti-AChR antibody without decremental RNS responses, and PD-L1 overexpression are possible characteristics shared by ICI-induced IM. Frequent thymoma association in patients with idiopathic IM and MG may suggest thymoma-related immunopathogenic mechanisms, including dysregulation of the immune checkpoint pathway.
Related collections
Most cited references28

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Atypical neurological complications of ipilimumab therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Myasthenic crisis and polymyositis induced by one dose of nivolumab
Author and article information
Contributors
-
This work was supported by Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Rare and Intractable Diseases (Validation of Evidence-based Diagnosis and Guidelines, and Impact on QOL in Patients with Neuroimmunological Diseases),Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI; 15K09347) from JSPS.
Journal
Affiliations
Author notes
Funding information and disclosures are provided at the end of the article. Full disclosure form information provided by the authors is available with the full text of this article at Neurology.org/NN.
Article
Publisher ID: NEURIMMINFL2018018416This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives License 4.0 (CC BY-NC-ND), which permits downloading and sharing the work provided it is properly cited. The work cannot be changed in any way or used commercially without permission from the journal.