- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Npro of Classical Swine Fever Virus Suppresses Type III Interferon Production by Inhibiting IRF1 Expression and Its Nuclear Translocation
Read this article at
Abstract
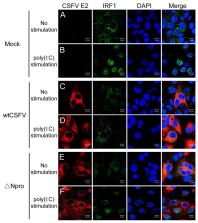
Classical swine fever virus (CSFV) causes a contagious disease of pigs. The virus can break the mucosal barrier to establish its infection. Type III interferons (IFN-λs) play a crucial role in maintaining the antiviral state in epithelial cells. Limited information is available on whether or how CSFV modulates IFN-λs production. We found that IFN-λ3 showed dose-dependent suppression of CSFV replication in IPEC-J2 cells. Npro-deleted CSFV mutant (∆Npro) induced significantly higher IFN-λs transcription from 24 h post-infection (hpi) than its parental strain (wtCSFV). The strain wtCSFV strongly inhibited IFN-λs transcription and IFN-λ3 promoter activity in poly(I:C)-stimulated IPEC-J2 cells, whereas ∆Npro did not show such inhibition. Npro overexpression caused significant reduction of IFN-λs transcription and IFN-λ3 promoter activity. Both wtCSFV and ∆Npro infection induced time-dependent IRF1 expression in IPEC-J2 cells, with ΔNpro showing more significant induction, particularly at 24 hpi. However, infection with wtCSFV or Npro overexpression led not only to significant reduction of IRF1 expression and its promoter activity in poly(I:C)-treated IPEC-J2 cells but also to blockage of IRF1 nuclear translocation. This study provides clear evidence that CSFV Npro suppresses IRF1-mediated type III IFNs production by inhibiting IRF1 expression and its nuclear translocation.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found