- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Freezing of gaze during action preparation under threat imminence
Read this article at
Abstract
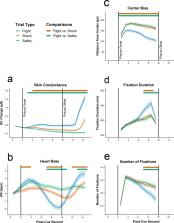
When confronted with threatening stimuli, animals typically respond with freezing behavior characterized by reduced movement and heart rate deceleration. Freezing-like responses during threat anticipation have also been observed in humans and are associated with anxiety. Recent evidence yet suggests that freezing does not necessarily reflect helpless immobility but can also aid the preparation of a threat escape. To investigate which further behavioral responses human freezing encompasses, we presented 50 young adults (10 male) with aversive stimuli that could sometimes be avoided while measuring gaze, cardiovascular and electrodermal activity. In trials in which the threat could be escaped, participants displayed reduced heart rate, increased electrodermal activity and reduced visual exploration. Furthermore, heart rate deceleration and restricted visual exploration predicted the speed of flight responses. These results provide evidence for freezing behavior in measures of visual exploration and suggest that such responding is adaptive in preparing the subsequent escape of approaching threats.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neural organization of the defensive behavior system responsible for fear.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.