- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Levels of organochlorine pesticides in onion and tomato samples from selected towns of Jimma Zone, Ethiopia
Read this article at
Abstract
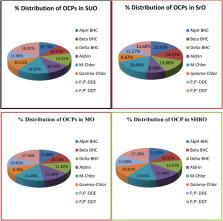
This study aimed to determine residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in tomato and onion samples collected from selected markets in the Jimma zone. A QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) method was used for sample preparation followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for OCPs analysis. The method used showed wide linear ranges from 5-50 μg/L for all eight pesticides, with R 2 values ≥ 0.992. The LOD values for the pesticides tested ranged from 0.14 μg/kg for p,p'-DDE to 2.40 μg/kg for p,p-DDT. LOQ values ranged from 0.46 μg/kg for p,p-DDE to 8.32 μg/kg for p,p'-DDT. The recoveries ranged from 74.84 – 109.45 % except for β-BHC (67.82 %). While most of the OCPs in the onion and tomato samples met European Union (EU) and Codex standards, some exceeded the limits. Methoxychlor and p,p'-DDT in onions, and methoxychlor, p,p'-DDT, α-BHC, and δ-BHC in some tomatoes, were detected above the permitted levels. Specific OCPs were not detected in some samples including aldrin in Meki Tomato (Mek-T), γ-chlordane in Agaro Tomato (Ag-T), and p,p'-DDE in Gera Tomato (Ger-T). The residual concentrations of OCPs varied among the samples. Among tomatoes, Gera had the highest percentage of detected OCPs contaminants (37 %), followed by Agaro (34.34 %) and Meki (28.55 %). Similarly, Sire onion (SrO) had the highest percentage of detected OCPs (28 %) compared to Minjer (25.16 %), Shewa Robit (25.10 %), and Sudan onion (22.25 %). In conclusion, most tomato and onion samples analyzed in this study contained OCP residues highlighting the importance of conducting a consumer health risk assessment.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A review of the global pesticide legislation and the scale of challenge in reaching the global harmonization of food safety standards.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Review of pesticide residue analysis in fruits and vegetables. Pre-treatment, extraction and detection techniques

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found