- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Physicochemical Properties of Restructured Black Goat Jerky with Various Types of Ultra-Ground Seaweed Powders
Read this article at
Abstract
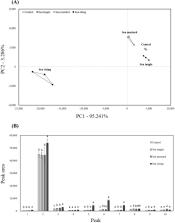
This study investigated the effects of ultra-ground seaweed powders (USP) on the physicochemical properties (proximate composition, mineral contents, pH, color, shear force, sensory evaluation, electronic nose, and electronic tongue) of restructured black goat jerky. Restructured black goat jerky was prepared using three different treatments, i.e., 3% (w/w) each of ultra-ground sea tangle (ST; Undaria pinnatifida), sea mustard (SM; Saccharina japonica), and sea string (SS; Gracilaria verrucosa) powders. Moisture and ash contents were significantly higher in the USP-treated group than in the control (p<0.05). Potassium, calcium, and zinc contents were significantly higher in the SM than in the other USP-treated groups (p<0.05). In contrast, pH values were significantly higher in the ST and SM than in the control and SS (p<0.05). CIE L*, CIE a*, CIE b*, and shear force were significantly lower in the USP-treated groups than in the control (p<0.05). Sensory evaluation revealed no significant difference in taste, texture, seaweed-like odor, and goaty flavor (p<0.05). Principal component analysis (PCA) and peak graph analysis of the electronic nose showed that the SS differed the most from the control compared with the other USP-treated groups, owing to the seaweed odor of ultra-ground SS powder. The PCA and ranking analysis of the electronic tongue showed that the umami taste of the SM was higher than that of the control and other USP-treated groups. Therefore, the potassium, calcium, zinc contents, and umami taste of reconstituted black goat jerky were significantly higher in the SM than in the control and other USP-treated groups.
Related collections
Most cited references52
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Seaweeds as a Functional Ingredient for a Healthy Diet
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found