- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Timing and volume of transfusion for adult major trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock: a registry-based cohort study
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Transfusion of blood components is vital for the resuscitation of injured patients in hemorrhagic shock. Delays in initiating transfusion have been associated with harm, as has excess transfusion. The aim of this study was to evaluate variables associated with hospital mortality, with a focus on the two modifiable risk factors— time to initiate transfusion and volume of blood components—with hospital mortality.
Methods
This was a registry-based cohort study, including all consecutive adult patients presenting with hemorrhagic shock (systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≤90 mm Hg and transfusion of blood components) to a level 1 adult trauma center during a 5-year period (January 1, 2017–December 31, 2021). Associations with hospital mortality were assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis, with final models developed using backward elimination.
Results
There were 195 patients included and there were 49 (25.1%) in-hospital deaths. The median time to first transfusion was 10 (IQR 6–16) minutes. Age (adjusted OR (aOR) 1.06; 95% CI: 1.03 to 1.08), initial SBP (aOR 0.96; 95% CI: 0.3 to 0.98), intracranial bleeding or diffuse axonal injury (aOR 2.63; 95% CI: 1.11 to 6.23), and the volume of blood components in the first 4 hours (aOR 1.08; 95% CI: 1.03 to 1.13) were associated with mortality. Time to transfusion was not associated with in-hospital mortality (aOR 0.99; 95% CI: 0.95 to 1.03). Among the 90 patients who underwent urgent transfer to the operating room or angiography suite, the median time to transfer was 2.38 hours (IQR 1.5–3.7). In this subgroup, age (aOR 1.11; 95% CI: 1.05 to 1.18) and volume of blood components (aOR 1.20; 95% CI: 1.08 to 1.34) were associated with mortality.
Discussion
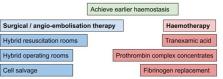
In this setting where times to transfusion are short, further reductions in the time to transfusion are unlikely to improve outcome. In our population, for every unit of blood component transfused, the adjusted odds of death increased by 8%. These findings suggest investigation into strategies to achieve earlier control of hemorrhage.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Every minute counts
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found