- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Stretch-induced actin remodeling requires targeting of zyxin to stress fibers and recruitment of actin regulators
Read this article at
Abstract
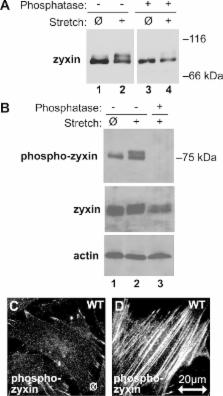
Mechanical stimulation induces zyxin-dependent actin cytoskeletal reinforcement. Stretch induces MAPK activation, zyxin phosphorylation, and recruitment to actin stress fibers, independent of p130Cas. Zyxin's C-terminal LIM domains are required for stretch-induced targeting to stress fibers, and zyxin's N-terminus is necessary for actin remodeling.
Abstract
Reinforcement of actin stress fibers in response to mechanical stimulation depends on a posttranslational mechanism that requires the LIM protein zyxin. The C-terminal LIM region of zyxin directs the force-sensitive accumulation of zyxin on actin stress fibers. The N-terminal region of zyxin promotes actin reinforcement even when Rho kinase is inhibited. The mechanosensitive integrin effector p130Cas binds zyxin but is not required for mitogen-activated protein kinase–dependent zyxin phosphorylation or stress fiber remodeling in cells exposed to uniaxial cyclic stretch. α-Actinin and Ena/VASP proteins bind to the stress fiber reinforcement domain of zyxin. Mutation of their docking sites reveals that zyxin is required for recruitment of both groups of proteins to regions of stress fiber remodeling. Zyxin-null cells reconstituted with zyxin variants that lack either α-actinin or Ena/VASP-binding capacity display compromised response to mechanical stimulation. Our findings define a bipartite mechanism for stretch-induced actin remodeling that involves mechanosensitive targeting of zyxin to actin stress fibers and localized recruitment of actin regulatory machinery.
Related collections
Most cited references69
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms of mechanotransduction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
