- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparing Preferences for Disease Profiles: A Discrete Choice Experiment from a US Societal Perspective
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
There is increasing interest in expanding the elements of value to be considered when making health policy decisions. To help inform value frameworks, this study quantified preferences for disease attributes in a general public sample and examined which combination of attributes (disease profiles) are considered most important for research and treatment.
Methods
A discrete choice experiment (DCE) was conducted in a US general population sample, recruited through online consumer panels. Respondents were asked to select one of a set of health conditions they believed to be most important, characterized by attributes defined by a previous qualitative study: onset age; cause of disease; life expectancy; caregiver requirement; symptom burden (characterized by the Health Utilities Index with varying levels of ambulation independence, dexterity limitations, and degree of pain and discomfort); and disease prevalence. A fractional factorial DCE design was implemented using R, and 60 choice sets were generated (separated into blocks of 10 per participant). Data were analyzed using a mixed-logit regression model, and results used to assess the likelihood of preferring disease profiles. Based on individual attribute preferences, overall preferences for disease profiles, including a profile aligned with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), were compared.
Results
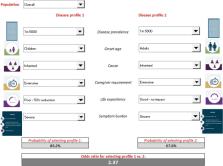
Fifty-two percent of respondents ( n = 537) were female, and 70.6% were aged 18–54 years. Attributes considered most important were those related to life expectancy (odds ratio [OR], 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.88 [1.56–2.27] for a 50% reduction in remaining life expectancy vs no impact), and symptom burden (OR [95% CI] 1.84 [1.47–2.31] for severe vs mild burden). Greater importance was also found for pediatric onset, caregiver requirement, and diseases affecting more people. As an example of disease profile preferences, a DMD-like pediatric inherited disease with 50% reduction in life expectancy, extensive caregiver requirement, severe symptom burden, and 1:5000 prevalence had 2.37-fold higher odds of being selected as important versus an equivalent disease with adult onset and no life expectancy reduction.
Conclusions
Of disease attributes included in this DCE, respondents valued higher prevalence of disease, life expectancy and symptom burden as most important for prioritizing research and treatment. Based on expressed attribute preferences, a case study of an inherited pediatric disease involving substantial reductions to length and quality of life and requiring caregiver support has relatively high odds of being identified as important compared to diseases reflecting differing attribute profiles. These findings can help inform expansions of value frameworks by identifying important attributes from the societal perspective.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Conjoint analysis applications in health--a checklist: a report of the ISPOR Good Research Practices for Conjoint Analysis Task Force.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and neuromuscular, rehabilitation, endocrine, and gastrointestinal and nutritional management
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found