- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Raman Spectroscopy: Guiding Light for the Extracellular Matrix
Read this article at
Abstract
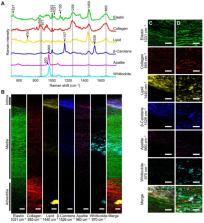
The extracellular matrix (ECM) consists of a complex mesh of proteins, glycoproteins, and glycosaminoglycans, and is essential for maintaining the integrity and function of biological tissues. Imaging and biomolecular characterization of the ECM is critical for understanding disease onset and for the development of novel, disease-modifying therapeutics. Recently, there has been a growing interest in the use of Raman spectroscopy to characterize the ECM. Raman spectroscopy is a label-free vibrational technique that offers unique insights into the structure and composition of tissues and cells at the molecular level. This technique can be applied across a broad range of ECM imaging applications, which encompass in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo analysis. State-of-the-art confocal Raman microscopy imaging now enables label-free assessments of the ECM structure and composition in tissue sections with a remarkably high degree of biomolecular specificity. Further, novel fiber-optic instrumentation has opened up for clinical in vivo ECM diagnostic measurements across a range of tissue systems. A palette of advanced computational methods based on multivariate statistics, spectral unmixing, and machine learning can be applied to Raman data, allowing for the extraction of specific biochemical information of the ECM. Here, we review Raman spectroscopy techniques for ECM characterizations over a variety of exciting applications and tissue systems, including native tissue assessments (bone, cartilage, cardiovascular), regenerative medicine quality assessments, and diagnostics of disease states. We further discuss the challenges in the widespread adoption of Raman spectroscopy in biomedicine. The results of the latest discovery-driven Raman studies are summarized, illustrating the current and potential future applications of Raman spectroscopy in biomedicine.
Related collections
Most cited references109
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Raman spectroscopy of proteins: a review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Raman spectroscopy of lipids: a review
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found