- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Protective effect of Gastrodia elata Blume in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease based on network pharmacology
Read this article at
Abstract
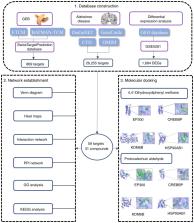
The aim of the present study was to investigate the protective effect of Gastrodia elata Blume (GEB) against Caenorhabditis elegans ( C. elegans) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) through network pharmacology. Firstly, the active constituents of GEB through ETCM and BATMAN-TCM databases were collected and its potential AD-related targets in Swiss Target Prediction were predicted. The potential targets related to AD were collected from the GeneCards, OMIM, CTD and DisGeNET databases, and the differential genes (DEGs) between the normal population and the AD patient population in GSE5281 chip of the Gene Expression Omnibus database were collected at the same time. The intersection of the three targets yielded 59 key targets of GEB for the treatment of AD. The drug-active ingredient-target-AD network diagram was constructed and visualized with Cytoscape software to obtain the core components. Subsequently, protein-protein interaction analysis (PPI) was performed on 59 key targets through STRING database, and Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses was performed on 59 key targets. Finally, molecular docking was conducted between core components and core targets using AutoDock software, and the C. elegans AD model was used for experimental verification to explore the regulatory paralysis effect of core components on the C. elegans model, β-amyloid (Aβ) plaque deposition, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction verification of the regulatory effect of components on targets. The GEB components 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl methane (DM) and protocatechuic aldehyde (PA) were found to be most strongly associated with AD, and five core targets were identified in the PPI network, including GAPDH, EP300, HSP90AB1, KDM6B, and CREBBP. In addition to GAPDH, the other four targets were successfully docked with DM and PA using AutoDock software. Compared with the control group, 0.5 mM DM and 0.25 mM PA significantly delayed C. elegans paralysis (P<0.01), and inhibited the aggregation of Aβ plaques in C. elegans. Both DM and PA could upregulate the expression level of core target gene HSP90AB1 (P<0.01), and DM upregulated the expression of KDM6B (P<0.01), suggesting that DM and PA may be potential active components of GEB in the treatment of AD.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found