- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Psychosis risk among pregnant women in Ghana
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Psychotic illness, although is rare, has been reported in the perinatal period. Individuals diagnosed with psychotic illness tend to first exhibit psychotic-like experiences (PLEs), defined as subclinical psychotic symptoms that occur outside the context of sleep or drug use. However, there is a paucity of empirical data on PLEs in pregnancy to advance scholarly discourse and support professional practice. The current study investigated the prevalence and correlates of PLEs among pregnant women in Ghana, a West African state.
Design
A cross-sectional survey design was used to collect data from 702 pregnant women who responded to measures of PLEs, COVID-19 concerns and behavioral maladies such as anxiety and depressive symptoms. Descriptive and inferential statistics, namely chi square, exploratory factor analysis, MANOVA and multinomial logistic regression were used to analyze the data.
Results
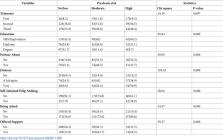
The results showed that 54.2%, 27.3% and 18.5% of participants were at no/low, moderate and high risk for psychosis, respectively. A total of 44.4% participants were not distressed by PLEs, whereas 32.2% and 23.4% were a bit/quite and very distressed, respectively. Psychosis risk was elevated among pregnant women who were more concerned about the COVID-19 effects, scored high in suicidal ideation, depressive symptoms and sleep difficulties.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found