- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Predictive Factors of Recurrence for Multifocal Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma With Braf v600e Mutation: A Single Center Study of 1,207 Chinese Patients
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: The American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines risk stratify Braf v600e mutated multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (BMPTMC) into different recurrence risk groups by the extent of extrathyroidal extension (ETE). These findings and modifications for BMPTMC need to be verified in additional studies.
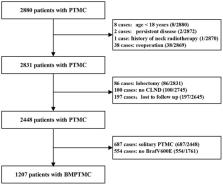
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted in BMPTMC patients who underwent total thyroidectomy (TT) and central lymph node dissection (CLND) from 2008 to 2013. Overall, 1,207 patients were included, and predictive factors were identified by univariate and multivariate analysis over a mean 7.5-year follow up.
Results: BMPTMC with ETE to capsule shows the same recurrence rate (3.8%) with intrathyroidal BMPTMC. Moreover, BMPTMC with ETE only to strap muscle, which belongs to high-risk group according to ATA guideline, shows relatively lower recurrence rate (13.3%) compared with some intermediate risk categories such as cN1 and >5 pN1. Multivariate analysis using a Cox proportional hazards regression model shows that total tumor diameter (TTD) is associated with significantly higher recurrence for BMPTMC with or without other risk factors (Hazard Ratio (HRO) = 9.86 [95%CI 5.35–18.20], p = 0.00; HRO = 2.32 [95%CI 1.12–4.85], p = 0.02; respectively), while Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT) is found to be protective against the recurrence (HRO = 0.51 [95%CI 0.33–0.79], p = 0.00; HRO = 0.47 [95%CI 0.25–0.89], p = 0.02; respectively).
Conclusions: Taken together, capsular ETE and gross ETE to the strap muscles did not have the expected significant influence on recurrence for Chinese BMPTMC patients who underwent TT and CLND. Rather than the extent of ETE, TTD and the lack of HT were identified as predictors for recurrence among BMPTMC with or without other risk factors (vascular invasion, cN1, pN1>5, pN1>3 cm).
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Association between BRAF V600E mutation and mortality in patients with papillary thyroid cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer: pathogenic role, molecular bases, and clinical implications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found