- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association between dairy consumption and the risk of diabetes: A prospective cohort study from the China Health and Nutrition Survey
Read this article at
Abstract
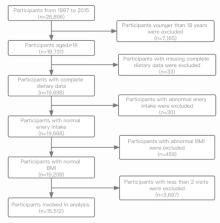
Diet is closely related to the risk of diabetes; yet the relationship between dairy consumption and the risk of diabetes is unclear with conflicting evidence from previous studies. This study used data from the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey to investigate the association between dairy consumption and diabetes. A total of 15,512 adults were included; dairy consumption at each survey was assessed by the 3-day 24-h recall and weighed food record methods, and diabetes occurrence was derived from self-reported information. The association between dairy consumption and diabetes was explored using Cox regression and further stratified with BMI and energy intake. Results indicated that 12,368 (79.7%) participants had no dairy consumption, while 2,179 (14.0%) and 947 (6.1%) consumed dairy at 0.1–100 and >100 g/day, respectively. After adjusting for potential confounders, dairy consumption of 0.1–100 g/day was associated with lower risk of diabetes in all participants (HR 0.53, 95% CI:0.38 −0.74; P < 0.001) and males (HR 0.50, 95% CI: 0.31–0.80; P = 0.004). According to the restricted cubic splines (RCS), the protective effect on diabetes was significant in the total population with dairy consumption ranging from 25 to 65 g/day (HR <1, P = 0.025). In the stratified analysis, consuming 30–80 g/day was associated with reduced diabetes risk among the ≤ 2,000 kcal/day energy intake group (HR <1, P = 0.023). In conclusion, dairy consumption was inversely associated with a reduced diabetes risk in Chinese population. Further studies are required to examine the optimal level of dairy consumption for preventing diabetes in the Chinese population.
Related collections
Most cited references60
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence and Ethnic Pattern of Diabetes and Prediabetes in China in 2013.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found