- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Portable Brain-Computer Interface for the Intensive Care Unit Patient Communication Using Subject-Dependent SSVEP Identification
Read this article at
Abstract
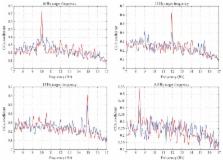
A major predicament for Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients is inconsistent and ineffective communication means. Patients rated most communication sessions as difficult and unsuccessful. This, in turn, can cause distress, unrecognized pain, anxiety, and fear. As such, we designed a portable BCI system for ICU communications (BCI4ICU) optimized to operate effectively in an ICU environment. The system utilizes a wearable EEG cap coupled with an Android app designed on a mobile device that serves as visual stimuli and data processing module. Furthermore, to overcome the challenges that BCI systems face today in real-world scenarios, we propose a novel subject-specific Gaussian Mixture Model- (GMM-) based training and adaptation algorithm. First, we incorporate subject-specific information in the training phase of the SSVEP identification model using GMM-based training and adaptation. We evaluate subject-specific models against other subjects. Subsequently, from the GMM discriminative scores, we generate the transformed vectors, which are passed to our predictive model. Finally, the adapted mixture mean scores of the subject-specific GMMs are utilized to generate the high-dimensional supervectors. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed system achieved 98.7% average identification accuracy, which is promising in order to provide effective and consistent communication for patients in the intensive care.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Paresis acquired in the intensive care unit: a prospective multicenter study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Human EEG responses to 1-100 Hz flicker: resonance phenomena in visual cortex and their potential correlation to cognitive phenomena.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found