- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anti-gout Potential of Malaysian Medicinal Plants
Read this article at
Abstract
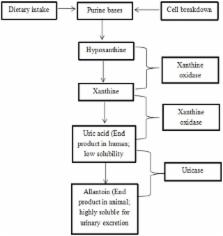
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes painful inflammation in one or more joints. In gout, elevation of uric acid in the blood triggers the formation of crystals, causing joint pain. Malaysia is a mega-biodiversity country that is rich in medicinal plants species. Therefore, its flora might offer promising therapies for gout. This article aims to systematically review the anti-gout potential of Malaysian medicinal plants. Articles on gout published from 2000 to 2017 were identified using PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar with the following keyword search terms: “gout,” “medicinal plants,” “Malaysia,” “epidemiology,” “ in vitro,” and “ in vivo.” In this study, 85 plants were identified as possessing anti-gout activity. These plants had higher percentages of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity (>85%); specifically, the Momordica charantia, Chrysanthemum indicum, Cinnamomum cassia, Kaempferia galanga, Artemisia vulgaris , and Morinda elliptica had the highest values, due to their diverse natural bioactive compounds, which include flavonoids, phenolics, tannin, coumarins, luteolin, and apigenin. This review summarizes the anti-gout potential of Malaysian medicinal plants but the mechanisms, active compounds, pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and safety of the plants still remain to be elucidated.
Related collections
Most cited references91
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular identification of a renal urate anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found