- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Immune-related ureteritis and cystitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: Case report and literature review
Read this article at
Abstract
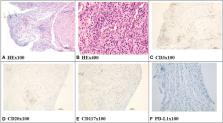
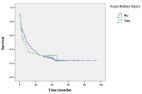
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (anti-CTLA4) and anti-programmed death cell protein 1 (anti-PD-1), are increasingly prescribed in metastatic carcinoma therapy. ICI-related kidney injury is gradually recognized by clinicians. However, immune-related ureteritis and cystitis easily go undiagnosed. We report three cases of PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb)-related ureteritis and cystitis. We further carried out a review of the literature about ICI-related ureteritis and cystitis. The cases in our reports manifest urinary irritation, sterile pyuria, gross hematuria, hydronephrosis, dilation of the ureters, and acute kidney injury. Urinary irritation improved effectively; urinalysis and renal function returned to normal after glucocorticoid therapy. During ICI therapy, urinalysis and renal function and urinary imaging examination are recommended to be monitored regularly. It contributes to identify immune-related ureteritis/cystitis earlier to efficiently alleviate urinary symptoms and immunologic urinary tract injury through glucocorticoid therapy while avoiding the abuse of antibiotics.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: ASCO Guideline Update
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found