- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The impact of physical activity on psychological health during Covid-19 pandemic in Italy

Read this article at
Abstract
The worldwide spread of COVID-19 has upset the normality of Italian daily life, forcing population to social distancing and self-isolation. Since the containment precautions also concern sport-related activities, home workout remained the only possibility to play sports and stay active during the pandemic.
The present study aimed to examine changes in the physical activity levels during self-quarantine in Italy, and the impact of exercise on psychological health.
A total of 2974 Italian subjects has completed an online survey, but only 2524 subjects resulted eligible for this study. The questionnaire measured the total weekly physical activity energy expenditure before and during quarantine (i.e. the sum of walking, moderate-intensity physical activities, and vigorous-intensity physical activities) in Metabolic Equivalent Task minutes per week (MET–min/wk) using an adapted version of International Physical Activity Questionnaire and their psychological well-being using the Psychological General Well Being Index. Of the 2524 Italian subjects included in the study, 1426 were females (56.4%) and 1098 males (43.6%). Total physical activity significantly decreased between before and during COVID-19 pandemic (Mean: 2429 vs. 1577 MET–min/wk, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001), in all age groups and especially in men (Female, mean: 1994 vs. 1443 MET–min/wk, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; Male, mean: 2998 vs. 1754 MET–min/wk, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Furthermore, a significant positive correlation was found between the variation of physical activity and mental well-being (r = 0.07541, ∗∗∗p = 0.0002), suggesting that the reduction of total physical activity had a profoundly negative impact on psychological health and well-being of population.
Based on this scientific evidence, maintaining a regular exercise routine is a key strategy for physical and mental health during a forced rest period like the current coronavirus emergency.
Abstract
Exercise; Epidemiology; Public health; Psychology; COVID-19; Pandemic; Quarantine; Physical activity; Home based exercise; IPAQ-SF; Psychological well-being; PGWBI.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
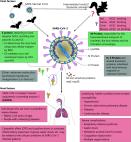
A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
