- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Progress in Polymeric Nano-Medicines for Theranostic Cancer Treatment
Read this article at
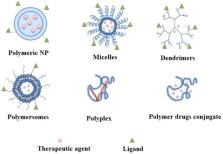
Abstract
Cancer is a life-threatening disease killing millions of people globally. Among various medical treatments, nano-medicines are gaining importance continuously. Many nanocarriers have been developed for treatment, but polymerically-based ones are acquiring importance due to their targeting capabilities, biodegradability, biocompatibility, capacity for drug loading and long blood circulation time. The present article describes progress in polymeric nano-medicines for theranostic cancer treatment, which includes cancer diagnosis and treatment in a single dosage form. The article covers the applications of natural and synthetic polymers in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Efforts were also made to discuss the merits and demerits of such polymers; the status of approved nano-medicines; and future perspectives.
Related collections
Most cited references218
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preparation of polymers with controlled molecular architecture. A new convergent approach to dendritic macromolecules
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Imaging and drug delivery using theranostic nanoparticles.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.