- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Deciphering the potential anti-COVID-19 active ingredients in Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees by combination of network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics†

Read this article at
Abstract
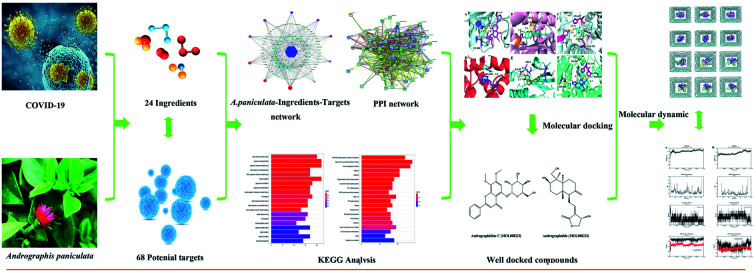
Currently, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 has posed an enormous threat to public health worldwide. An andrographolide sulfonates preparation, named Xiyanping injection in Chinese, which was prepared from the aqueous extract of Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees, showed favorable therapeutic effectiveness on COVID-19, suggesting A. paniculata could contain powerful therapeutic ingredients against COVID-19. In this study, to search for the potential drug candidates for COVID-19 in the herb, 68 potential target proteins and 24 active ingredients from A. paniculata were screened out using TCMSP, STP, Genecards and TTD databases firstly. A. paniculata-Compound-Target network constructed by cytoscape software showed that the protein targets PTGS2, EGFR, MAPK14, etc. had a high network relevance value. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that the 24 compounds in A. paniculata might exert their therapeutic effects by the biological processes, cellular response to biotic stimulus, response to lipopolysaccharide, response to molecule of bacterial origin, etc. And AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications (hsa04933), Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection (hsa05167), Human cytomegalovirus infection (hsa05163), etc. were predicted as the most significant effect pathways. Andrographidine C (MOL008223) and andrographolide (MOL008232) were found with strong binding affinity to the target active sites of the potential targets by molecular docking. Ultimately, the application of molecular dynamics simulations demonstrated that andrographidine C could bind well to the ACE2 and PIK3CG proteins. This research identified novel molecules against COVID-19 for developing natural medicines from A. paniculate and also provides a possible explanation for the molecular mechanisms of Xiyanping Injection against COVID-19.
Abstract
An integrated approach of network pharmacology, molecular docking and molecular dynamics to decipher the potential anti COVID-19 active ingredients in Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees.