- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nanocarriers-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems for Anticancer Agents: An Overview and Perspectives
Abstract
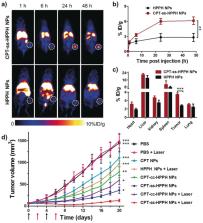
Nanotechnology has been actively integrated as drug carriers over the last few years to treat various cancers. The main hurdle in the clinical management of cancer is the development of multidrug resistance against chemotherapeutic agents. To overcome the limitations of chemotherapy, the researchers have been developing technological advances for significant progress in the oncotherapy by enabling the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents at increased drug content levels to the targeted spots. Several nano-drug delivery systems designed for tumor-targeting are evaluated in preclinical and clinical trials and showed promising outcomes in cancerous tumors’ clinical management. This review describes nanocarrier’s importance in managing different types of cancers and emphasizing nanocarriers for drug delivery and cancer nanotherapeutics. It also highlights the recent advances in nanocarriers-based delivery systems, including polymeric nanocarriers, micelles, nanotubes, dendrimers, magnetic nanoparticles, solid lipid nanoparticles, and quantum dots (QDs). The nanocarrier-based composites are discussed in terms of their structure, characteristics, and therapeutic applications in oncology. To conclude, the challenges and future exploration opportunities of nanocarriers in chemotherapeutics are also presented.
Most cited references157

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found