- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Stress of COVID-19 and mental health outcomes in Palestine: the mediating role of well-being and resilience
Read this article at
Abstract
BACKGROUND
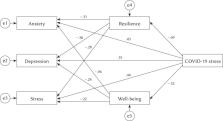
We tested the association between the stress of COVID-19 and mental distress manifested by anxiety, depression, and stress, and whether well-being and resilience mediate the relationship between the two variables in a population of Palestinian adults. Namely, we hypothesized that stress of COVID-19 will be positively associated with mental health problems (anxiety, depression, and stress); well-being and resilience will be negatively associated with mental health problems (anxiety, depression, and stress); and well-being and resilience will mediate the association between the stress of COVID-19 and mental health problems (anxiety, depression, and stress).
PARTICIPANTS AND PROCEDURE
Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale-21, the Resilience Scale for Adults, the WHO-5 Well-Being Index, and the COVID-19 Stress Scales were administered to 860 participants via online survey. Structural equation modelling (SEM) was applied to address the study hypothesis.
RESULTS
Participants recorded a mild level of stress of COVID-19 and high scores for resilience and well-being. A conceptual model depicting COVID-19 stress as a predictor, mental distress as an outcome variable, and resilience and subjective well-being as mediators was confirmed.
CONCLUSIONS
Palestinians are exposed to mental distress in an environment characterized by ongoing stressors. Conversely, the capability of Palestinians to conserve good levels of well-being and resilience protects them from mental distress even in the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak. On the other hand, COVID-19 can be considered a new critical event demanding and diminishing the people’s resiliency recourses in Palestine. Implications for clinical practice and research are discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references60
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found