- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Emerging evidence have illustrated the vital role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) on the human cancer progression and tumorigenesis. However, the role of LINC00511 in breast cancer tumourigenesis is still unknown. This research puts emphasis on the function of LINC00511 on the breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness, and investigates the in-depth mechanism.
Methods
The lncRNA and RNA expression were measured using RT-PCR. Protein levels were measured using western blotting analysis. CCK-8, colony formation assays and transwell assay were performed to evaluate the cell proliferation ability and invasion. Sphere-formation assay was also performed for the stemness. Bioinformatic analysis, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and luciferase reporter assays were carried to confirm the molecular binding.
Results
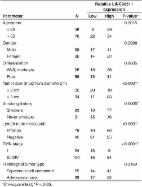
LINC00511 was measured to be highly expressed in the breast cancer specimens and the high-expression was correlated with the poor prognosis. Functionally, the gain and loss-of-functional experiments revealed that LINC00511 promoted the proliferation, sphere-formation ability, stem factors (Oct4, Nanog, SOX2) expression and tumor growth in breast cancer cells. Mechanically, LINC00511 functioned as competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-185-3p to positively recover E2F1 protein. Furthermore, transcription factor E2F1 bind with the promoter region of Nanog gene to promote it transcription.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00511 Acts as an Oncogene in Non–small-cell Lung Cancer by Binding to EZH2 and Suppressing p57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
