- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Unprotected Anal Intercourse with Regular Male Sex Partners among HIV Negative Men Who Have Sex with Men in China: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Read this article at
Abstract
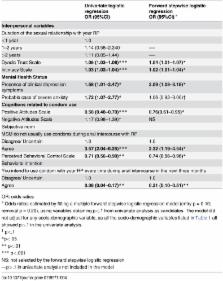
The HIV prevalence and incidence among men who have sex with men (MSM) in China are high. Unprotected anal intercourse (UAI) with a regular male sex partner (RP), a significant predictor of HIV sero-conversion, was high yet under-emphasized among MSM having RP (MSMRP). The present cross-sectional survey interviewed 307 HIV negative MSMRP recruited through convenient sampling from multiple sources, including venue-based outreaching, online recruitment, and referrals made by peers, in Beijing and Chengdu, China. Among MSMRP, the prevalence of UAI with RP in the last three months was 52.4%. The results of the multivariate analysis showed that trust and intimacy within the relationship with RP and presence of clinical depression symptoms were positively associated with UAI with RP in the last three months. Other associated scalar factors derived from the Theory of Planned Behavior were related to perceptions on condom use, including positive attitudes toward condom use (a negative association), subjective norm of the perception that MSM do not usually use condoms during anal intercourse with RP (a positive association), perceived behavioral control over condom use with RP (a negative association), and behavioral intention to use condoms with RP in the coming three months (a negative association). It is seen that MSMRP were at high risk of HIV/STD transmission. The associated factors hence involved those related to perceptions about condom use, mental health, and interpersonal relationship. Future interventions should take these multi-dimensional factors into account. In particular, future research to test the efficacy of couple-based interventions that include mental health elements needs to be conducted, as trust and intimacy within the relationship were associated with UAI among MSMRP, and mental health problems may exist for both the MSMRP and their RP.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Sexual agreements among gay male couples.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Stigma, social context, and mental health: lesbian and gay couples across the transition to adoptive parenthood.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found