- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Development and validation of a preoperative nomogram for predicting positive surgical margins after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Positive surgical margins are independent risk factor for biochemical recurrence, local recurrence, and distant metastasis after radical prostatectomy. However, limited predictive tools are available. This study aimed to develop and validate a preoperative nomogram for predicting positive surgical margins after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP).
Methods
From January 2010 to March 2016, a total of 418 patients who underwent LRP without receiving neoadjuvant therapy at Peking University Third Hospital were retrospectively involved in this study. Clinical and pathological results of each patient were collected for further analysis. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression (backward stepwise method) were used for the nomogram development. The concordance index (CI), calibration curve analysis and decision curve analysis were used to evaluate the performance of our model.
Results
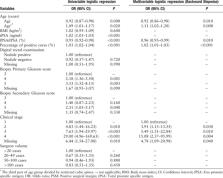
Of 418 patients involved in this study, 142 patients (34.0%) had a positive surgical margin on final pathology. Based on the backward selection, four variables were included in the final multivariable regression model, including the percentage of positive cores in preoperative biopsy, clinical stage, free prostate specific antigen (fPSA)/total PSA (tPSA), and age. A nomogram was developed using these four variables. The concordance index (C-index) of the nomogram was 0.722 in the development cohort and 0.700 in the bootstrap validations. The bias-corrected calibration plot showed a limited departure from the ideal line with a mean absolute error of 2.0%. In decision curve analyses, the nomogram showed net benefits in the range from 0.2 to 0.7.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adjuvant radiotherapy for pathological T3N0M0 prostate cancer significantly reduces risk of metastases and improves survival: long-term followup of a randomized clinical trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found