- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
High Titer of Acquired Factor V Inhibitor Presenting with a Pseudo-deficiency of Multiple Coagulation Factors
Read this article at
Abstract
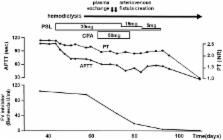
Acquired coagulation factor inhibitor is a rare coagulation disorder. We herein report a patient with acquired factor V inhibitor showing a decrease in multiple coagulation factor activities. A high titer of factor V inhibitor presumably led to a marked inhibition of factor V activity in the specific factor-deficient plasma used in coagulation factor activity assays based on either an activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) or prothrombin time (PT) clotting assay, resulting in false low values of the coagulation activity. We re-examined the coagulation factor activity using several dilutions of the patient's plasma and confirmed that the high factor V inhibitor titer had caused an apparent decrease in multiple coagulation factor activities.
Related collections
Most cited references14
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Factor V deficiency: a concise review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found