- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Monoamine Oxidase A Inhibitors–Indocyanine Dyes Conjugates as Targeted Antitumor Agents
Read this article at
Abstract
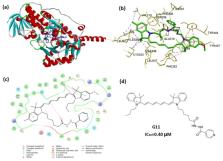
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) is an important mitochondria-bound enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters. Accumulating evidence suggests a significant association of increased MAOA expression and advanced high-grade prostate cancer (PCa) progression and metastasis. Herein, a series of novel conjugates combining the MAOA inhibitor isoniazid (INH) and tumor-targeting near-infrared (NIR) heptamethine cyanine dyes were designed and synthesized. The synthesized compounds G1– G13 were evaluated in vitro for their cytotoxicity against PC-3 cells using the MTT assay, and molecular docking studies were performed. Results showed that most tested compounds exhibited improved antitumor efficacy compared with INH. Moreover, conjugates G10 and G11 showed potent anticancer activity with IC 50 values (0.85 and 0.4 μM respectively) comparable to that of doxorubicin (DOX). This may be attributable to the preferential accumulation of these conjugates in tumor cells. G10, G11, and G12 also demonstrated moderate MAOA inhibitory activities. This result and the results of molecular docking studies were consistent with their cytotoxicity activities. Taken together, these data suggest that a combination of the MAOA inhibitor INH with tumor-targeting heptamethine cyanine dyes may prove to be a highly promising tool for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Translation of near-infrared fluorescence imaging technologies: emerging clinical applications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A molecular correlate to the Gleason grading system for prostate adenocarcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found