- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Glabridin induces paraptosis-like cell death via ER stress in breast cancer cells
Read this article at
Abstract
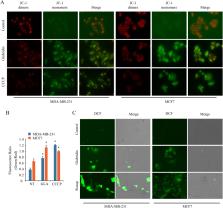
Glabridin, a polyphenolic flavonoid isolated from the root of the glycyrrhiza glabra, has been demonstrated to have anti-tumor properties in human malignancies. This study found that glabridin decreased the viability of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 cells in a dose-dependent manner that was not involved in the caspase-3 cascade. Glabridin promoted the formation of extensive cytoplasmic vacuolation by increasing the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers BiP, XBP1s, and CHOP. The transmission electron microscopy and fluorescence with the ER chaperon KDEL suggested that the vacuoles were derived from ER. Glabridin-induced vacuolation was blocked when protein synthesis was inhibited by cycloheximide, demonstrating that protein synthesis is crucial for this process. Furthermore, we determined that glabridin causes loss of mitochondrial membrane potential as well as the production of reactive oxygen species, both of which lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. These features are consistent with a kind of programmed cell death described as paraptosis. This work reports for the first time that glabridin could induce paraptosis-like cell death, which may give new therapeutic approaches for apoptosis-resistant breast cancers.
Abstract
Glabridin; Paraptosis; ER stress; Vacuolation; Breast cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found