- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact on total population health and societal cost, and the implication on the actual cost-effectiveness of including tumour necrosis factor-α antagonists in management of ankylosing spondylitis: a dynamic population modelling study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Sequential treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) that includes tumour necrosis factor-α antagonists (anti-TNF agents) has been applied in most of the Western countries. Existing cost-effectiveness (CE) models almost exclusively presented the incremental CE of anti-TNF agents using a closed cohort while budget impact studies are mainly lacking. Notwithstanding, information on impact on total population health and societal budget as well as on actual incremental CE for a given decision time span are important for decision makers. This study aimed at quantifying, for different decision time spans starting from January 1, 2014 in the Dutch society, (1) impact of sequential drug treatment strategies without and with inclusion of anti-TNF agents (Strategies 1 and 2, respectively) on total population health and societal cost, and (2) the actual incremental CE of Strategy 2 compared to Strategy 1.
Methods
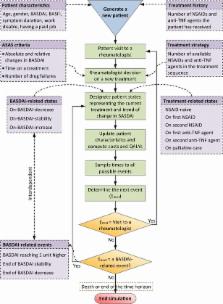
Dynamic population modelling was used to capture total population health and cost, and the actual incremental CE. Distinguishing the prevalent AS population on January 1, 2014 and the incident AS cohorts in the subsequent 20 years, the model tracked individually an actual number of AS patients until death or end of the simulation time. During the simulation, data on patient characteristics, history of drug use, costs and health at discrete time points were generated. In Strategy 1, five nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were available but anti-TNF agents withdrawn. In Strategy 2, five NSAIDs and two anti-TNF agents continued to be available.
Results
The predicted size of the prevalent AS population in the Dutch society varied within the range of 67,145–69,957 with 44–46 % of the patients receiving anti-TNF agents over the period 2014–2034. The use of anti-TNF agents resulted in an increase in the annual drug costs (168.54–205.28 million Euros), but at the same time caused a decrease in the annual productivity costs (12.58–31.21 million Euros) and in annual costs of healthcare categories other than drugs (7.23–11.90 million Euros). Incremental cost (Euros) per QALY gained in Strategy 2 compared to Strategy 1 corresponding to decision time spans of 5, 10, 15 and 20 years improved slightly from 75,379 to 67,268, 63,938 and 61,129, respectively. At willingness-to-pay thresholds of 118,656, 112,067, 110,188 and 110,512 Euros, it was 99 % certain that Strategy 2 was cost-effective for decision time spans of 5, 10, 15 and 20, respectively.
Conclusions
Using the dynamic population approach, the present model can project real-time data to inform a healthcare system decision that affects all actual number of AS patients eligible for anti-TNF agents within different decision time spans. The predicted total population costs of different categories in the present study can help plan the organization of the healthcare resources based on the national budget for the disease.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Book: not found
Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27 positive and negative blood donors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found