- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
“Self” and “other”: A conceptual bridge linking normal with pathological personality
Read this article at
Abstract
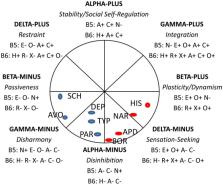
The goal of this paper is to try and close the gap between the ways in which pathological and normal personality, including their development, are conceptualized. To this end, attention is drawn to parallels that exist between the ways self-function is conceptualized in contemporary personality psychology and in recent iterations of the major psychiatric nosologies, particularly ICD-11. Conceptualizations in both normal and abnormal personality see a fundamental dichotomy between self as identity and self as socially interdependent (vs autonomous). Evidence is reviewed supporting a basic dichotomy between two categories of personality pathology that can be subsumed under the labels “Acting Out” and “Anxious-Inhibited.” It is suggested that fundamental to the personality pathology subsumed under “Acting Out” is a deficient interdependent self, while a defective self-identity is proposed to underlie the personality pathology subsumed under “Anxious-Inhibited.”
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Are traits useful? Explaining trait manifestations as tools in the pursuit of goals.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found