- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Padrão temporal, distribuição espacial e fatores associados a incidência de HIV/AIDS entre jovens no Brasil Translated title: Temporal pattern, spatial distribution, and factors associated with the incidence of HIV/AIDS among young people in Brazil Translated title: Patrón temporal, distribución espacial y factores asociados a la incidencia de la infección por el VIH/sida en jóvenes en Brasil
RESUMO
Objetivo.
Descrever o padrão temporal e espacial e identificar os fatores associados a incidência de HIV/AIDS entre jovens no Brasil.
Método.
Estudo ecológico que incluiu jovens brasileiros de 15 a 24 anos notificados com HIV/AIDS de 2001 a 2021. Utilizou-se o método joinpoint para a análise temporal. Aglomerados espaciais foram detectados pelos métodos Bayesiano, autocorrelação espacial, Getis-Ord Gi* e Varredura Scan. Quatro modelos de regressão não espacial e espacial foram usados para identificar fatores associados ao desfecho. Todas as análises estatísticas consideraram p < 0,05.
Resultados.
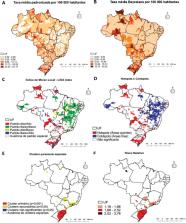
No Brasil, a incidência média foi de 12,29 por 100 000 habitantes, com aumento de 7,3% ao ano no período 2007-2014 e posterior decréscimo de 3,4% em 2014-2021. Observou-se padrão Alto/Alto e hotspots, principalmente em municípios do Sul, Sudeste, Centro-Oeste e Norte. O cluster primário localizou-se em 572 municípios do Rio Grande do Sul e Santa Catarina e os maiores riscos relativos em Manaus (Amazonas) e Rondonópolis (Mato Grosso). A taxa de analfabetismo (β = -0,08), Índice de GINI (β = -3,74) e Cobertura da Estratégia de Saúde da Família (β = -0,70) apresentaram relação negativa com o desfecho. Em contrapartida, o Índice Firjan de Desenvolvimento Municipal (β = 2,37), o Índice de Vulnerabilidade Social (β = 6,30), o percentual de pessoas que recebem o Bolsa Família (β = 0,04) e renda per capita (β = 0,008) apresentaram associação positiva.
Conclusão.
Houve tendência de aumento da incidência de HIV/AIDS até 2014 com posterior declínio até 2021. Aglomerados de altas taxas concentraram-se, especialmente, em municípios das regiões Norte, Sul, Sudeste e Centro-Oeste. Indicadores de vulnerabilidade socioeconômica influenciam o desfecho positivamente ou negativamente, dependendo do território investigado.
ABSTRACT
To describe temporal and spatial patterns and identify the factors associated with the incidence of HIV/AIDS among young people in Brazil.
Ecological study of young Brazilians aged 15-24 years with reported HIV/AIDS, from 2001 to 2021. The Joinpoint method was used for the temporal analysis. Spatial clusters were detected using Bayesian methods, spatial autocorrelation, Getis-Ord Gi*, and scan techniques. Four non-spatial and spatial regression models were used to identify factors associated with the result. All statistical analyses considered p < 0.05.
In Brazil, the average incidence was 12.29 per 100 000 inhabitants, with an annual increase of 7.3% in the period 2007-2014 and a subsequent 3.4% decrease in 2014-2021. A high-high pattern and hotspots were observed, mainly in municipalities in the South, Southeast, Central-West, and North regions. The primary cluster was located in 572 municipalities in Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina, with the highest relative risks in Manaus (Amazonas) and Rondonópolis (Mato Grosso). The illiteracy rate (β = -0.08), GINI Index (β = -3.74) and Family Health Strategy coverage (β = -0.70) were negatively associated with the result. In contrast, the Firjan Municipal Development Index (β = 2.37), Social Vulnerability Index (β = 6.30), percentage of Bolsa Família recipients (β = 0.04), and per capita income (β = 0.008) showed a positive association.
There was an upward trend in the incidence of HIV/AIDS until 2014, followed by a decline until 2021. High-rate clusters were concentrated in municipalities in the North, South, Southeast and Central-West regions in particular. Indicators of socioeconomic vulnerability had positive or negative effects on the result, depending on the territory investigated.
RESUMEN
Describir el patrón temporal y espacial, y determinar los factores asociados a la incidencia de infección por el VIH/sida en jóvenes en Brasil.
Estudio ecológico en jóvenes brasileños de 15 a 24 años con diagnóstico de infección por el VIH/sida en el período 2001-2021. Para el análisis temporal se utilizó el método de regresión de puntos de inflexión ( joinpoint). Los conglomerados espaciales se detectaron con métodos Bayesianos y de autocorrelación espacial, Gi* de Getis-Ord y escaneo. Se utilizaron cuatro modelos de regresión espacial y no espacial para detectar los factores asociados al resultado. En todos los análisis estadísticos se estableció un valor de p < 0,05 como umbral de significación.
En Brasil, la incidencia media fue de 12,29 por 100 000 habitantes, con un aumento del 7,3% anual en el período 2007-2014 y una reducción posterior del 3,4% en el período 2014-2021. Se observó un patrón alto/alto y la presencia de puntos calientes, principalmente en municipios del Sur, Sudeste, Centro-Oeste y Norte. El principal conglomerado se localizó en 572 municipios de Rio Grande do Sul y Santa Catarina, y los riesgos relativos más altos se observaron en Manaus (Amazonas) y Rondonópolis (Mato Grosso). La tasa de analfabetismo (β = -0,08), el índice de Gini (β = -3,74) y la cobertura de la estrategia de salud familiar (β = -0,70) mostraron una asociación negativa con el resultado. En cambio, el índice de Firjan de desarrollo municipal (β = 2,37), el índice de vulnerabilidad social (β = 6,30), el porcentaje de personas que reciben ayuda del programa de bienestar social Bolsa Família (β = 0,04) y los ingresos per cápita (β = 0,008) mostraron una asociación positiva.
Hubo una tendencia al aumento de la incidencia de infección por el VIH/sida hasta el 2014, con una reducción posterior hasta el 2021. Los conglomerados de tasas elevadas se concentraron especialmente en los municipios de las regiones Norte, Sur, Sudeste y Centro-Oeste. Los indicadores de vulnerabilidad socioeconómica tienen una influencia positiva o negativa en el resultado, según el territorio investigado.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Easy way to learn standardization : direct and indirect methods.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Adolescent lives matter: preventing HIV in adolescents
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found