- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
PCAT-1: A Novel Oncogenic Long Non-Coding RNA in Human Cancers
Read this article at
Abstract
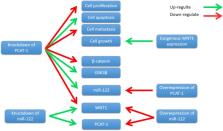
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides (nts) without obvious protein coding potential. lncRNAs act as multiple roles in biological processes of diseases, especially carcinomas. Prostate cancer associated transcript-1 (PCAT-1) is an oncogenic lncRNA that identified by RNA-Sequence in prostate cancer. High expression of PCAT-1 is observed in different types of cancers, including prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular cancer and gastric cancer. High expressed PCAT-1 is correlated with poor overall survival. Furthermore, PCAT-1 regulates cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Additionally, PCAT-1 is involved in EMT and Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway. In this review, we focus on the implication of PCAT-1 in human cancers.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long noncoding RNAs in cell-fate programming and reprogramming.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found