- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Spatial analysis of histology in 3D: quantification and visualization of organ and tumor level tissue environment
Read this article at
Abstract
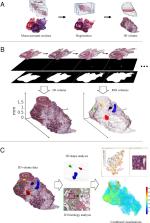
Histological changes in tissue are of primary importance in pathological research and diagnosis. Automated histological analysis requires ability to computationally separate pathological alterations from normal tissue. Conventional histopathological assessments are performed from individual tissue sections, leading to the loss of three-dimensional context of the tissue. Yet, the tissue context and spatial determinants are critical in several pathologies, such as in understanding growth patterns of cancer in its local environment. Here, we develop computational methods for visualization and quantitative assessment of histopathological alterations in three dimensions. First, we reconstruct the 3D representation of the whole organ from serial sectioned tissue. Then, we proceed to analyze the histological characteristics and regions of interest in 3D. As our example cases, we use whole slide images representing hematoxylin-eosin stained whole mouse prostates in a Pten+/- mouse prostate tumor model. We show that quantitative assessment of tumor sizes, shapes, and separation between spatial locations within the organ enable characterizing and grouping tumors. Further, we show that 3D visualization of tissue with computationally quantified features provides an intuitive way to observe tissue pathology. Our results underline the heterogeneity in composition and cellular organization within individual tumors. As an example, we show how prostate tumors have nuclear density gradients indicating areas of tumor growth directions and reflecting varying pressure from the surrounding tissue. The methods presented here are applicable to any tissue and different types of pathologies. This work provides a proof-of-principle for gaining a comprehensive view from histology by studying it quantitatively in 3D.
Abstract
Histology; 3D reconstruction; Quantitative imaging; Tissue analysis; Spatial analysis; Image analysis; Visualization
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found