- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Developing and validating a scale to measure Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) in elementary school children in Iran
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Food and nutrition literacy is an emerging term which is increasingly used in policy and research. Though research in this area is growing, progression is limited by the lack of an accepted method to measure food and nutrition literacy. The aim of this study is to develop a valid and reliable questionnaire to assess food and nutrition literacy in elementary school children in the city of Tehran.
Methods
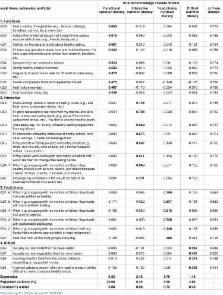
The study was conducted in three phases. To develop Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) questionnaire, a comprehensive literature review and a qualitative study were initially performed to identify food and nutrition literacy dimensions and its components. Content and face validity of the questionnaire were evaluated by an expert panel as well as students. In the second phase, construct validity of the scale was evaluated using Explanatory Factor Analyses (EFA) and Confirmatory Factor Analyses (CFA). In the last phase (confirmatory phase), the final version of the questionnaire was evaluated on 400 students.
Results
Findings show Content Validity Ratio (CVR) and Content Validity Index (CVI) of the 62-item questionnaire at acceptable levels of 0.87 and 0.92, respectively. EFA suggested a six-factor construct, namely, understanding food and nutrition information, knowledge, functional, interactive, food choice, and critical. The results of CFA indicated acceptable fit indices for the proposed models. All subscales demonstrated satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha≥0.70), except for critical skill subscale (0.48). The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC = 0.90, CI: 0.83–0.94) indicated that Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) scale had satisfactory stability. Each phase of development progressively improved the questionnaire, which resulted in a 46-item (42 likert-type items and 4 true-false items) Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) scale. The questionnaire measured two domains with 6 subscales, including: 1) cognitive domain: understanding and knowledge; 2) skill domain: functional, food choice, interactive, and critical skills.
Conclusion
The developed food and nutrition literacy scale is a valid and reliable instrument to measure food and nutrition literacy in children. This measure lays a solid empirical and theoretical foundation for future research and tailored interventions to promote food and nutrition literacy in this age group.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The nutrition transition: worldwide obesity dynamics and their determinants.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Instrument review: Getting the most from a panel of experts
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found