- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
miR-99a/100∼125b tricistrons regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell homeostasis by shifting the balance between TGFβ and Wnt signaling
Read this article at
Abstract
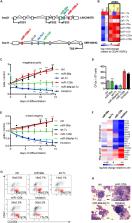
miR-99a/100, let-7, and miR-125b paralogs are encoded in two tricistrons and are highly expressed in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Emmrich et al. demonstrate that miR-99a/100∼125b tricistrons are transcribed as a polycistronic message and functionally converge at the combinatorial block of the TGFβ pathway. Down-regulating tumor suppressor genes APC/APC2 stabilized active β-catenin and enhanced Wnt signaling. These tricistronic miRNAs promoted sustained expansion of murine and human HSCs by switching the balance between Wnt and TGFβ signaling.
Abstract
Although regulation of stem cell homeostasis by microRNAs (miRNAs) is well studied, it is unclear how individual miRNAs genomically encoded within an organized polycistron can interact to induce an integrated phenotype. miR-99a/100, let-7, and miR-125b paralogs are encoded in two tricistrons on human chromosomes 11 and 21. They are highly expressed in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL), an aggressive form of leukemia with poor prognosis. Here, we show that miR-99a/100∼125b tricistrons are transcribed as a polycistronic message transactivated by the homeobox transcription factor HOXA10. Integrative analysis of global gene expression profiling, miRNA target prediction, and pathway architecture revealed that miR-99a/100, let-7, and miR-125b functionally converge at the combinatorial block of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) pathway by targeting four receptor subunits and two SMAD signaling transducers. In addition, down-regulation of tumor suppressor genes adenomatous polyposis coli ( APC)/ APC2 stabilizes active β-catenin and enhances Wnt signaling. By switching the balance between Wnt and TGFβ signaling, the concerted action of these tricistronic miRNAs promoted sustained expansion of murine and human HSCs in vitro or in vivo while favoring megakaryocytic differentiation. Hence, our study explains the high phylogenetic conservation of the miR-99a/100∼125b tricistrons controlling stem cell homeostasis, the deregulation of which contributes to the development of AMKL.
Related collections
Most cited references69
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
miRecords: an integrated resource for microRNA–target interactions
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found