- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dynamic nomogram for predicting acute kidney injury in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A retrospective study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
This study sought to develop and validate a dynamic nomogram chart to assess the risk of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
Methods
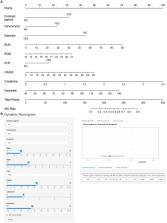
These data were drawn from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) database, which collects 47 clinical indicators of patients after admission to the hospital. The primary outcome indicator was the occurrence of AKI within 48 h of intensive care unit (ICU) admission. Independent risk factors for AKI were screened from the training set using univariate and multifactorial logistic regression analyses. Multiple logistic regression models were developed, and nomograms were plotted and validated in an internal validation set. Based on the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA) to estimate the performance of this nomogram.
Results
Nomogram indicators include blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, red blood cell distribution width (RDW), heart rate (HR), Oxford Acute Severity of Illness Score (OASIS), the history of congestive heart failure (CHF), the use of vancomycin, contrast agent, and mannitol. The predictive model displayed well discrimination with the area under the ROC curve values of 0.8529 and 0.8598 for the training set and the validator, respectively. Calibration curves revealed favorable concordance between the actual and predicted incidence of AKI ( p > 0.05). DCA indicates the excellent net clinical benefit of nomogram in predicting AKI.
Related collections
Most cited references47

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found