- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Collagen Promotes Higher Adhesion, Survival and Proliferation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Read this article at
Abstract
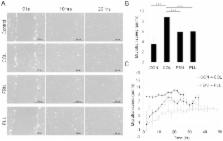
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can differentiate into several cell types and are desirable candidates for cell therapy and tissue engineering. However, due to poor cell survival, proliferation and differentiation in the patient, the therapy outcomes have not been satisfactory. Although several studies have been done to understand the conditions that promote proliferation, differentiation and migration of MSC in vitro and in vivo, still there is no clear understanding on the effect of non-cellular bio molecules. Of the many factors that influence the cell behavior, the immediate cell microenvironment plays a major role. In this context, we studied the effect of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in controlling cell survival, proliferation, migration and directed MSC differentiation. We found that collagen promoted cell proliferation, cell survival under stress and promoted high cell adhesion to the cell culture surface. Increased osteogenic differentiation accompanied by high active RHOA (Ras homology gene family member A) levels was exhibited by MSC cultured on collagen. In conclusion, our study shows that collagen will be a suitable matrix for large scale production of MSC with high survival rate and to obtain high osteogenic differentiation for therapy.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found