- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Progression-Free Survival for Liver Transplant vs Alternative Therapy in Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastasis
Read this article at
ScienceOpenPublisher
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
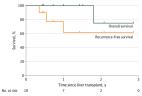
This cohort study compares survival outcomes between patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastasis who received chemotherapy-based multimodal therapy and patients who underwent liver transplant.
Related collections
Most cited references6
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Recipient and Donor Outcomes After Living-Donor Liver Transplant for Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Survival Benefit of Living-Donor Liver Transplant
Whitney E. Jackson, John Malamon, Bruce Kaplan … (2022)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Current State of Liver Transplantation for Colorectal Liver Metastases in the United States: A Call for Standardized Reporting
Kazunari Sasaki, Luis I. Ruffolo, Michelle H. Kim … (2023)