- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparison of optimised endovaginal vs external array coil T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging techniques for detecting suspected early stage (IA/IB1) uterine cervical cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
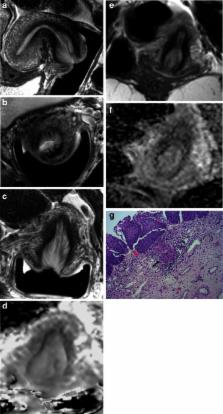
To compare sensitivity and specificity of endovaginal versus external-array coil T2-W and T2-W + DWI for detecting and staging small cervical tumours.
Methods
Optimised endovaginal and external array coil MRI at 3.0-T was done prospectively in 48 consecutive patients with stage Ia/Ib1 cervical cancer. Sensitivity/specificity for detecting tumour and parametrial extension against histopathology for a reading radiologist were determined on coronal T2-W and T2W + DW images. An independent radiologist also scored T2-W images without and with addition of DWI for the external-array and endovaginal coils on separate occasions >2 weeks apart. Cohen’s kappa assessed inter- and intra-observer agreement.
Results
Median tumour volume in 19/38 cases positive on subsequent histology was 1.75 cm 3. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV were: reading radiologist 91.3 %, 89.5 %, 91.3 %, 89.5 %, respectively; independent radiologist T2-W 82.6 %, 73.7 %, 79.1 %, 77.8 % for endovaginal, 73.9 %, 89.5 %, 89.5 %, 73.9 % for external-array coil. Adding DWI improved sensitivity and specificity of endovaginal imaging (78.2 %, 89.5 %); adding DWI to external-array imaging improved specificity (94.7 %) but reduced sensitivity (66.7 %). Inter- and intra-observer agreement on T2-W + DWI was good (kappa = 0.67 and 0.62, respectively).
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparison of endorectal coil and nonendorectal coil T2W and diffusion-weighted MRI at 3 Tesla for localizing prostate cancer: correlation with whole-mount histopathology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found