- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A systematic review of the incidence and prevalence of autoimmune disease in multiple sclerosis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
As new therapies emerge which increase the risk of autoimmune disease it is increasingly important to understand the incidence of autoimmune disease in multiple sclerosis (MS).
Objective:
The purpose of this review is to estimate the incidence and prevalence of comorbid autoimmune disease in MS.
Methods:
The PUBMED, EMBASE, SCOPUS and Web of Knowledge databases, conference proceedings, and reference lists of retrieved articles were searched, and abstracts were independently screened by two reviewers. The data were abstracted by one reviewer using a standardized data collection form, and the findings were verified by a second reviewer. We assessed quality of the included studies using a standardized approach and conducted meta-analyses of population-based studies.
Results:
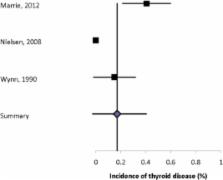
Sixty-one articles met the inclusion criteria. We observed substantial heterogeneity with respect to the populations studied, methods of ascertaining comorbidity, and reporting of findings. Based solely on population-based studies, the most prevalent autoimmune comorbidities were psoriasis (7.74%) and thyroid disease (6.44%). Our findings also suggest an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease, likely uveitis and possibly pemphigoid.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Alemtuzumab versus interferon beta 1a as first-line treatment for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomised controlled phase 3 trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epidemiology of autoimmune diseases in Denmark.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found