- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy and safety evaluation of Azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials
Read this article at
Abstract
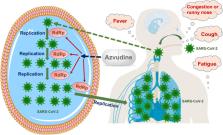
Azvudine (FNC) is a synthetic nucleoside analog used to treat adult patients living with human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection with high viral load. After phosphorylation, Azvudine inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, leading to the discontinuation of RNA chain synthesis in viruses. In addition, Azvudine is the first dual-target nucleoside oral drug worldwide to simultaneously target reverse transcriptase and viral infectivity factors in the treatment of HIV infection. On 9 August 2022, Azvudine was incorporated into the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (version ninth) issued by the National Health Commission and the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The recommended oral dose of Azvudine for the treatment of moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is 5 mg once daily, and the duration of Azvudine treatment should not exceed 14 days. Four phase III clinical trials were performed during 2020–2022 to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Azvudine in the treatment of COVID-19. The results revealed that Azvudine could reduce nucleic acid-negative conversion time, viral load, and time to improvement in clinical conditions in patients with moderate COVID-19. In addition, Azvudine exhibited good safety and tolerance. Thereafter, Azvudine was incorporated into the Chinese guidelines and expert consensus for the treatment of COVID-19 and was highly approbated. Furthermore, Azvudine was also included in the Chinese guidelines for HIV infection.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found